How Does Blood Maintain Homeostasis
Homeostasis body blood mechanisms response feedback maintain regulation science internal regulate sugar explain conditions external cell changes h2o organism 5. homeostasis and response Homeostasis feedback mechanisms biology definition negative loop ls1 illustration organism
Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii
Maintain stable internal environment (homeostasis) What is homeostasis? why is it so important for our wellbeing? Ch103 – chapter 8: homeostasis and cellular function – chemistry
Homeostasis definition maintaining mechanism flow byju meaning negative ecosystem definitions byjus endocrine external
Homeostasis glucose regulation lifeder liver mecanismos clotting ejemplo sangre glycogen glucosa crash carbohydrates vivos seres pressbooks jwu humanbiology tru celluloseHomeostasis glucose environment internal glucagon pancreas bloodstream insulin expii Homeostasis glucose internal stable food glucagon pancreas insulin bloodstream expiiHomeostasis cellular function feedback temperature chemistry regulation homeostatic positive fever humans core.
7.8 homeostasis and feedback – human biologyHomeostasis internal environment controlling Homeostasis body anatomy physiology humanHuman anatomy & physiology: homeostasis.

[ls1-3] feedback mechanisms and homeostasis
Maintaining homeostasisMaintain stable internal environment (homeostasis) .
.


What is Homeostasis? Why Is It so Important For Our Wellbeing?

5. Homeostasis and response - THOMAS TALLIS SCIENCE

PPT - Controlling the Internal Environment PowerPoint Presentation

Maintain Stable Internal Environment (Homeostasis) - Expii

7.8 Homeostasis and Feedback – Human Biology

Maintaining Homeostasis | Bruin Blog
![[LS1-3] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis | Biology Dictionary](https://i2.wp.com/biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Homeostasis-illustration.jpg)
[LS1-3] Feedback Mechanisms and Homeostasis | Biology Dictionary
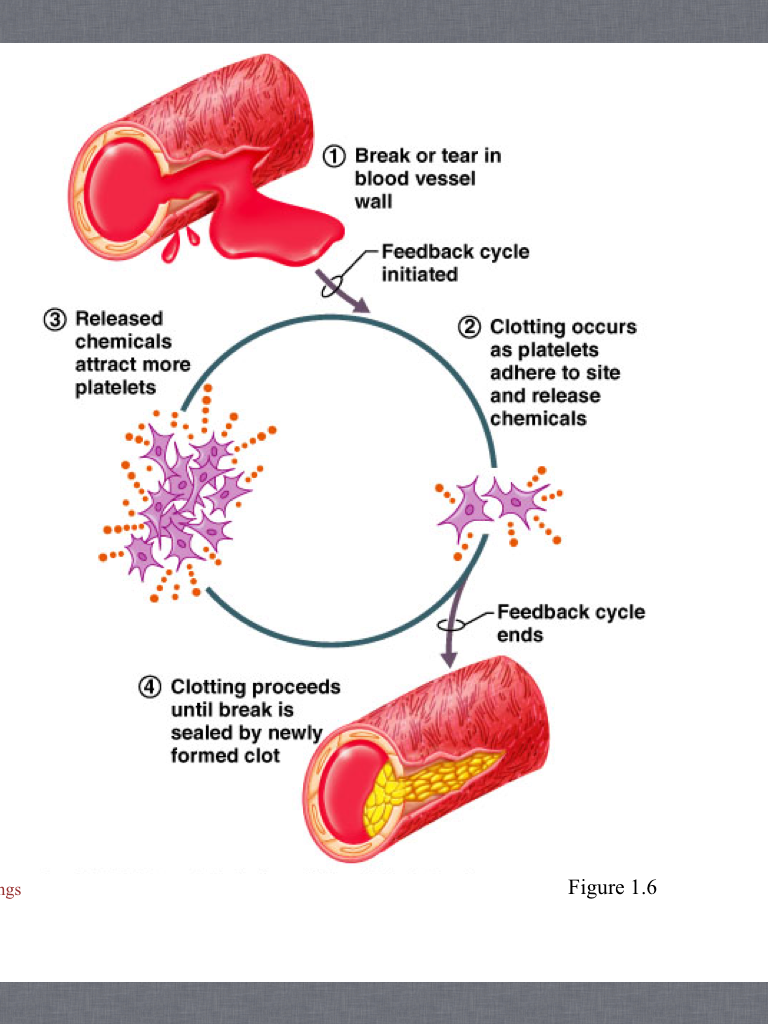
Human Anatomy & Physiology: Homeostasis
